.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
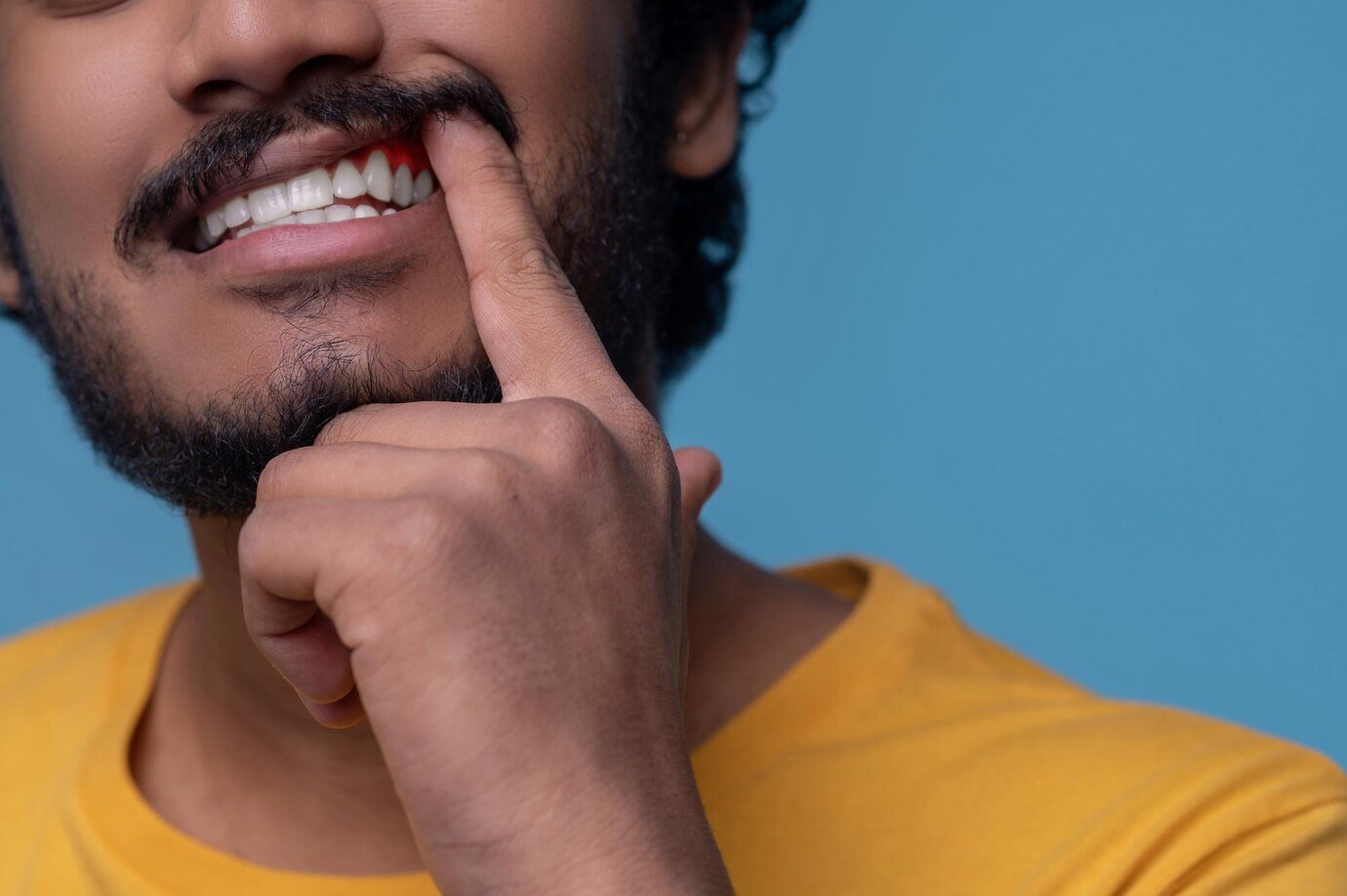

Gum Disease Treatment
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that's identifiable by symptoms such as gum inflammation, chronic bad breath and painful chewing. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 1 billion adults, or roughly 19% of the world's adult population, is affected by a severe form of gum disease.
Gum disease (also known as periodontal disease) has been associated with inflammatory processes and may be linked to certain systemic conditions. Below, we cover the various symptoms of gum disease and take you through the treatments available this 2026.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum diseases can be caused by various factors, including lifestyle and hygiene habits. Understanding these risk factors can help you better maintain gum health and reduce the risk of disease. These factors include:
- Abysmal oral hygiene. Irregular tooth brushing and/or incorrect brushing techniques can lead to the accumulation of bacteria and dental plaque (a sticky film composed of bacteria that forms on teeth), leading to gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Smoking. Smoking increases the risk of gum diseases as it impairs blood circulation and suppresses immunity, causing unpleasant breath that lingers.
- Sugary foods and drinks. Consuming large amounts of sugar-rich products can contribute to the formation of cavities and gum inflammation.
- Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Patients with diabetes are at increased risk of gum diseases due to metabolic disorders and reduced resistance to infections.
- Hormonal changes. Periods of hormonal fluctuations such as pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can increase gum sensitivity and exacerbate inflammatory processes.
- Stress. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making gums more vulnerable to inflammation.
- Genetic predisposition. Genetic factors can influence individual susceptibility to gum diseases.
- Clenching and grinding your teeth: Force from these actions may accelerate the rate at which the supporting tissues of the teeth are broken down.
- Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and/or Crohn's disease: When poorly managed, these can increase risk of infections, including periodontitis.
What Causes Gum Disease?

Gum Disease Stages
Gum disease can escalate from mild to severe, jeopardising the soft tissues and around teeth. Neglecting early treatment can lead from gingivitis to advanced periodontitis. Early identification and management may help slow disease progression and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
Gum Disease Stages
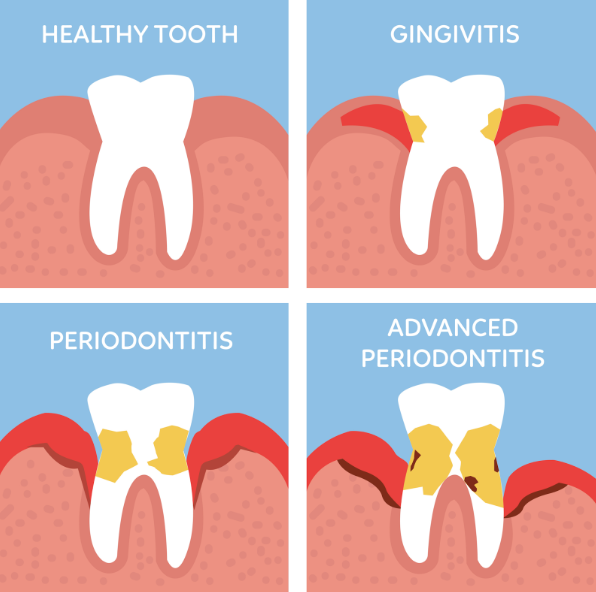
Gingivitis
Gingivitis, marked by gum inflammation, often results from poor oral hygiene and bacteria buildup. Symptoms include swollen, red, and bleeding gums, with possible pain and bad breath. Since gingivitis does not yet impact the bone and connective tissue that secure teeth, the condition may be reversible with appropriate oral hygiene and professional care. Treatment focuses on enhancing oral hygiene, regular dental cleanings, and using antiseptics to curb inflammation.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis, a more severe gum condition, occurs when inflammation spreads below the gum line, potentially causing pain, tooth loss, and abscesses. Treatment entails deep cleaning, managing gum pockets (spaces that form between the teeth and gums where bacteria can accumulate, leading to periodontitis), and antibiotics or surgery in advanced cases.
Advanced Periodontitis
As its name implies, advanced periodontitis is an advanced gum disease that’s also the most critical stage, leading to substantial tissue and bone loss. It manifests as deep gum pockets and tooth mobility. Management might require surgery, restorative procedures, or prosthetics to address tooth loss. Maintaining oral hygiene is essential for prevention.
Acute Necrotising Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
Occasionally, a rare condition known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) may arise abruptly. The symptoms of ANUG are typically more intense than standard gum disease symptoms and can encompass:
- Gums that bleed and are painful
- Painful sores
- Gums receding between teeth
- Foul breath
- A metallic flavour in the mouth
- Increased saliva production
- Challenges in swallowing or speaking
- Elevated body temperature (fever)
A clinical assessment is required to accurately diagnose and manage this condition.
Acute Necrotising Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum diseases can manifest with various symptoms, serving as key indicators of oral health issues. It's important to recognise diverse symptoms that may signal this condition. If you notice one or more of these symptoms, be sure to seek medical attention.
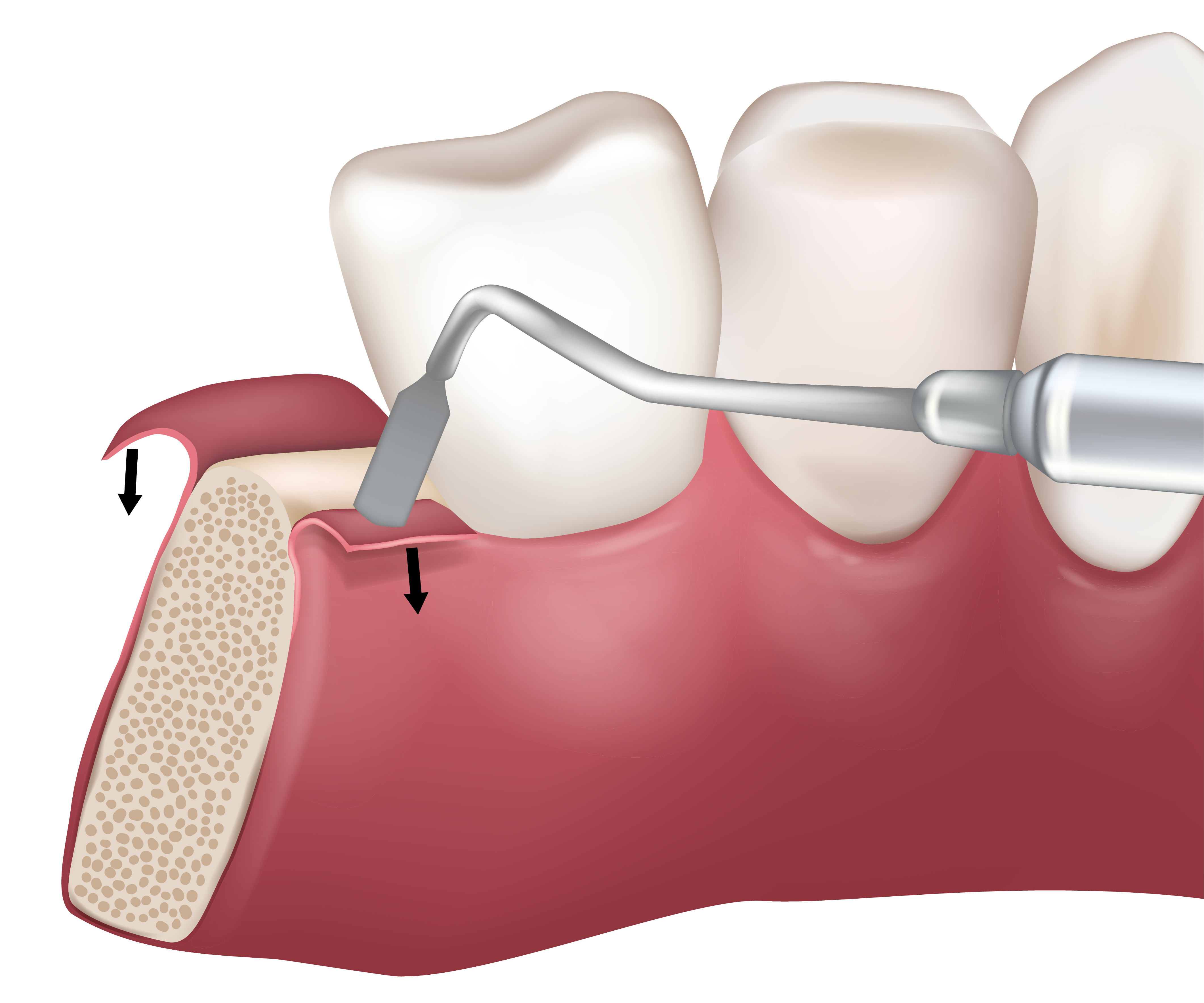
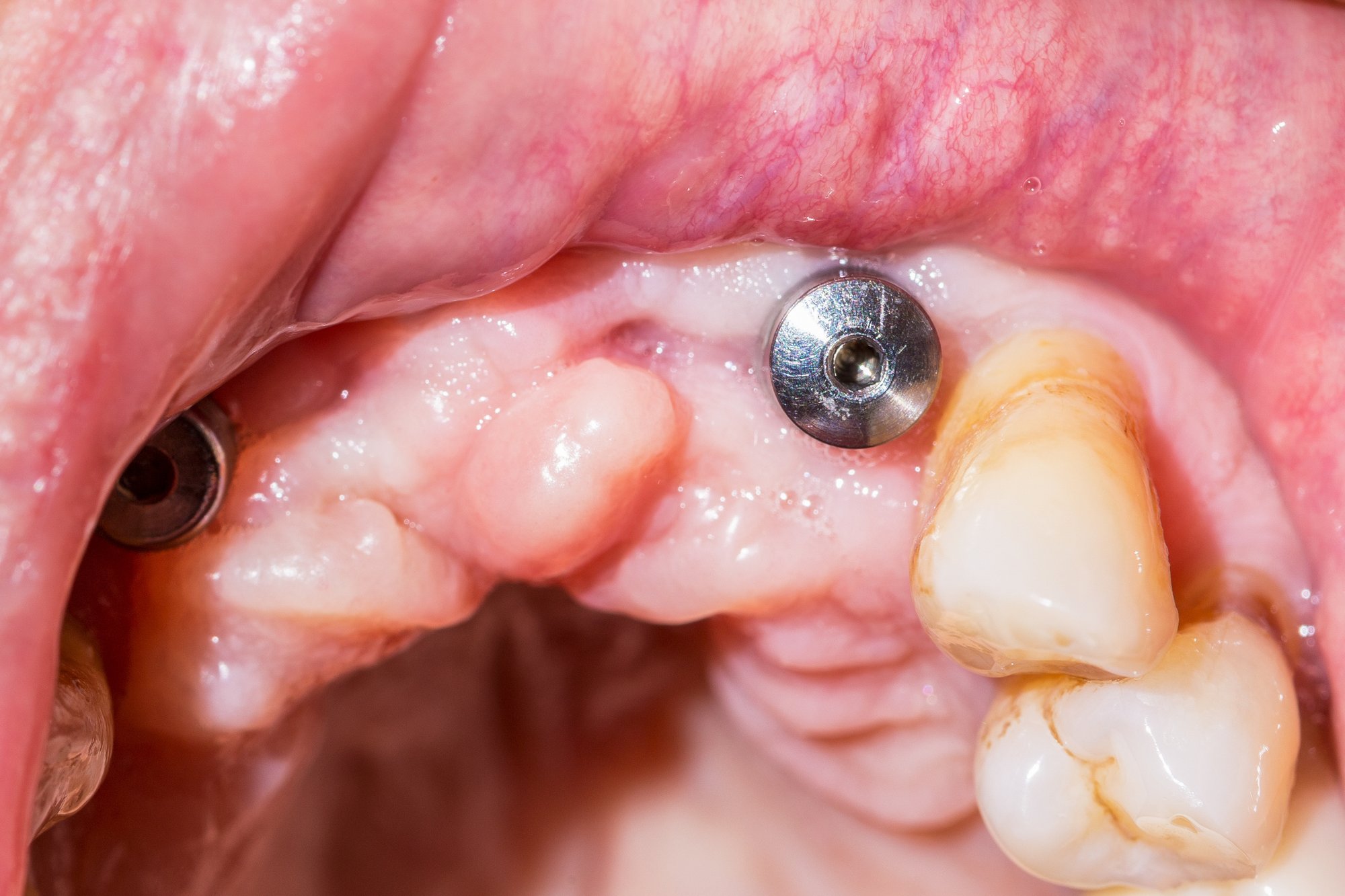
Gum Recession
Gum recession can create new spaces between teeth, affecting the overall structure of the oral cavity. Other signs indicating recession include:
- Visibility of tooth roots: When gums recede, tooth roots may become visible.
- Changes in the appearance of gums: They may appear red, inflamed, or thinner than usual.
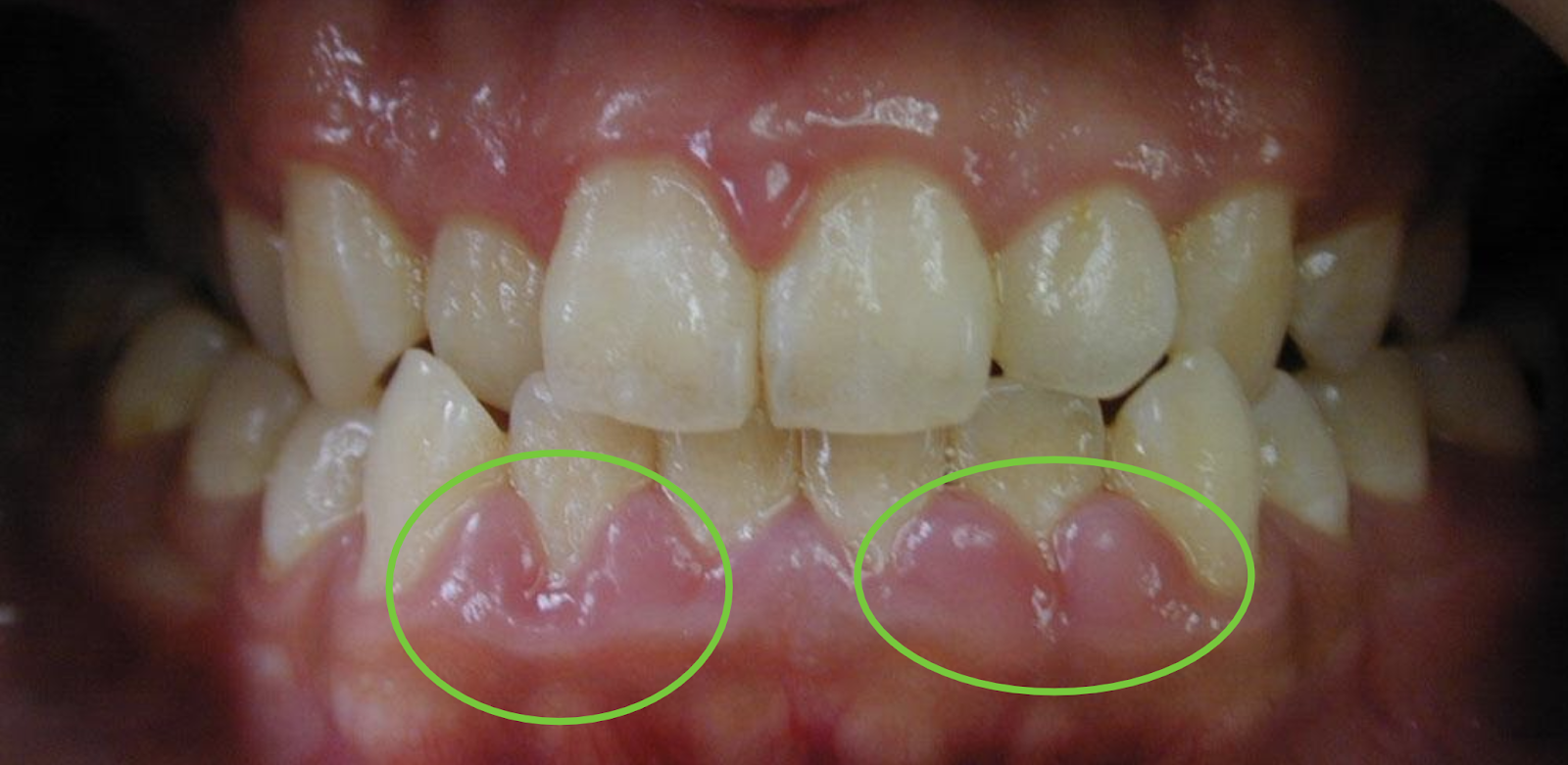
Gum Inflammation
Gum inflammation, characterised by redness and swelling, indicates an active inflammatory process. This could be associated with factors such as the accumulation of plaque and high levels of bacteria.
Pinkish Hue on Toothbrush After Brushing
If you notice visible blood on your toothbrush after brushing, pay attention to the condition of your gums – it may be a sign of gingivitis. Gums affected by gum disease are tender and thus more susceptible to damage.
Change in Bite Alignment
Gum diseases can lead to changes in bite alignment and result in improper alignment of teeth. Often, as gum disease develops and causes pain and bleeding, individuals may alter their chewing habits. This adjustment typically involves using different teeth than usual for chewing, which can contribute to issues like teeth shifting and further changes in bite alignment. These alterations can have a significant impact on overall dental health.
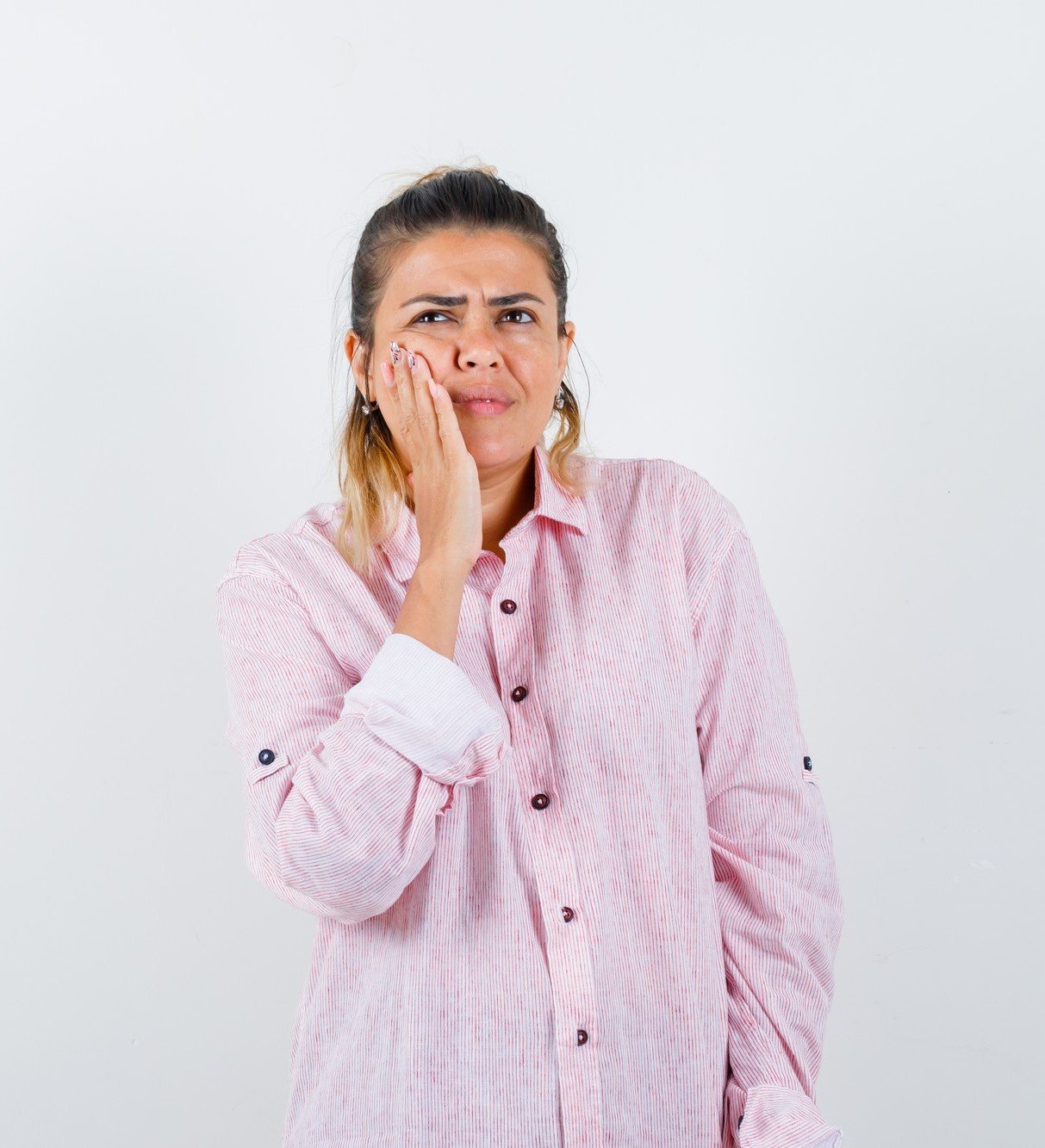
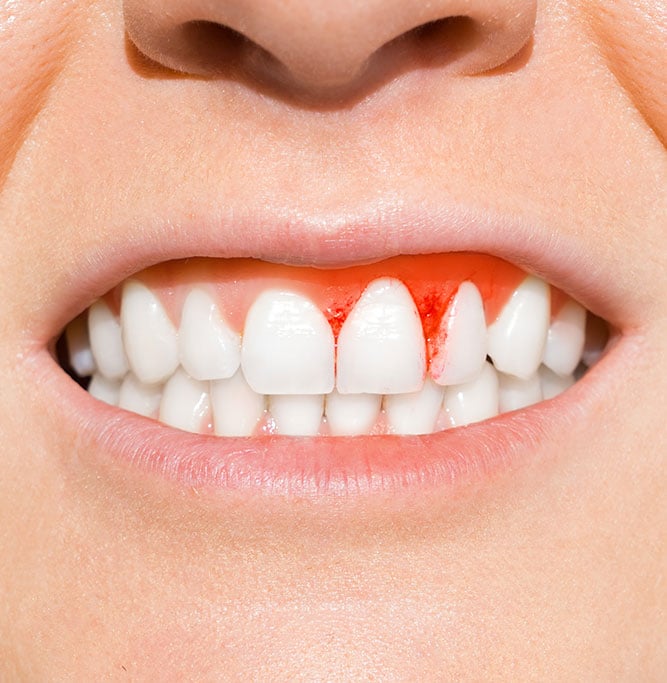
Swollen, Tender & Bleeding Gums
One of the first signs of gum problems is swelling, tenderness, and bleeding gums. These symptoms often indicate the presence of gingivitis, the initial stage of the periodontal disease.
Chronic Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath despite oral care efforts can be a sign of periodontal disease, especially if pus formations are present. If you’re thorough with hygiene upkeep and have no issues with digestion, this may be associated with gum disease.
Painful Chewing
Gum disease can make it painful to chew, especially hard or fibrous foods. This may lead people to eat softer, often sugary foods, which can worsen gum disease and potentially lead to more serious conditions like severe periodontitis.
Pus Between Teeth and Gums
The presence of pus between the teeth and gums can be a sign of infection which should be assessed by a dental professional. Prompt treatment will help prevent the spread of infection, preserve the tooth, and restore gum health.
Loss of Teeth
In the advanced stages of periodontitis, the deterioration of dental and gum tissues can lead to tooth loss. As the gums weaken, their ability to support the teeth roots diminishes. This weakening causes the teeth to become loose and, over time, can result in the eventual loss of teeth.
A qualified dentist will help you to prevent gum disease from progressing further. For deep cleaning, schedule an appointment with a specialist.
Gum Disease Treatment Options in 2026
Treatment for gum diseases encompasses a wide range of methods to eliminate inflammation and restore damaged tissues. The methods used vary depending on the complexity and stage of the disease.
Non-Surgical Treatments
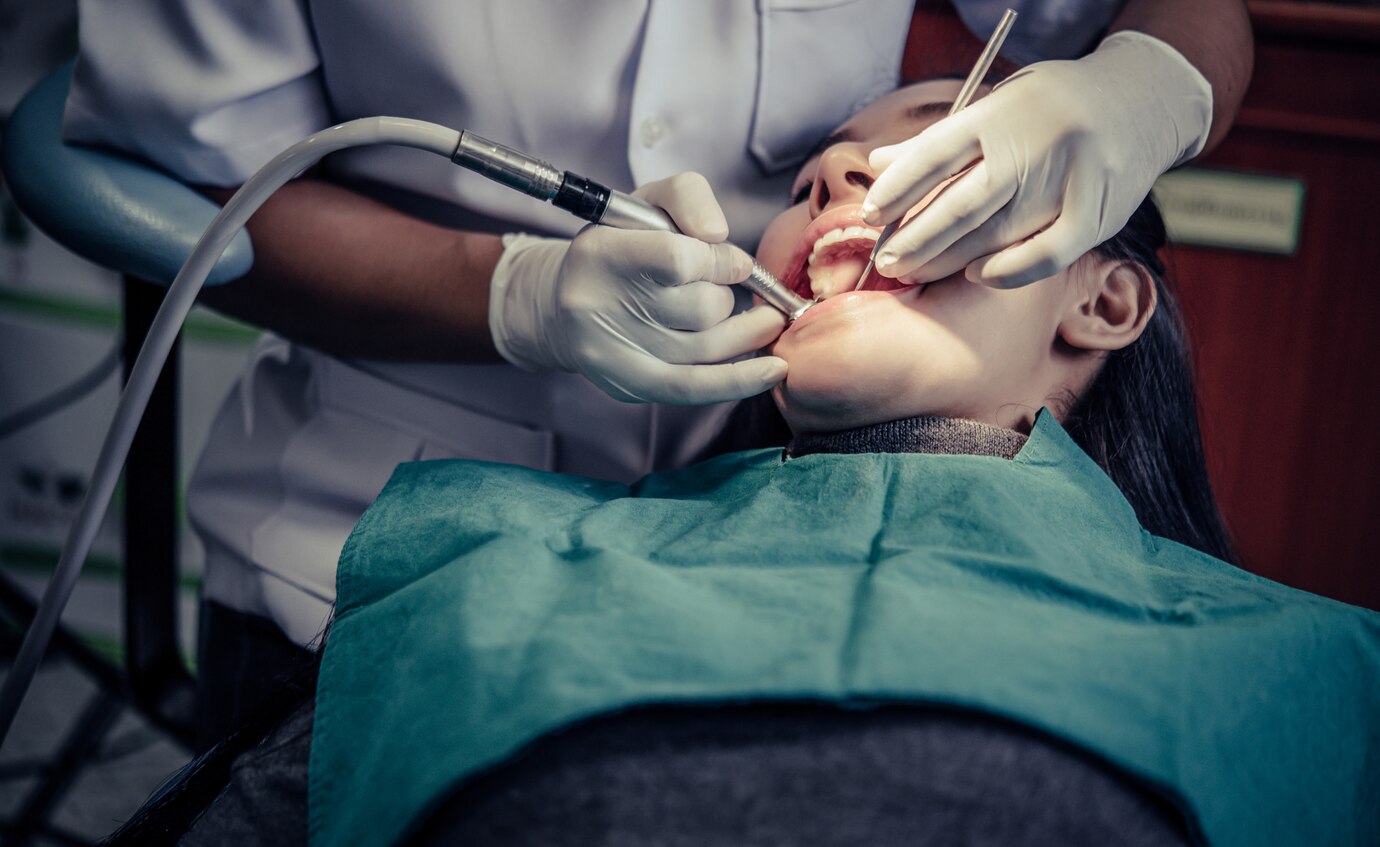
Scaling and Polishing
Regular scaling and polishing, beyond personal hygiene routines, are essential in preventing gum diseases. These cleanings remove plaque and tartar (hardened dental plaque that forms on teeth) build-up inaccessible by daily brushing and flossing, keeping gums healthy and preventing the progression of periodontal disease.
Scaling and Polishing
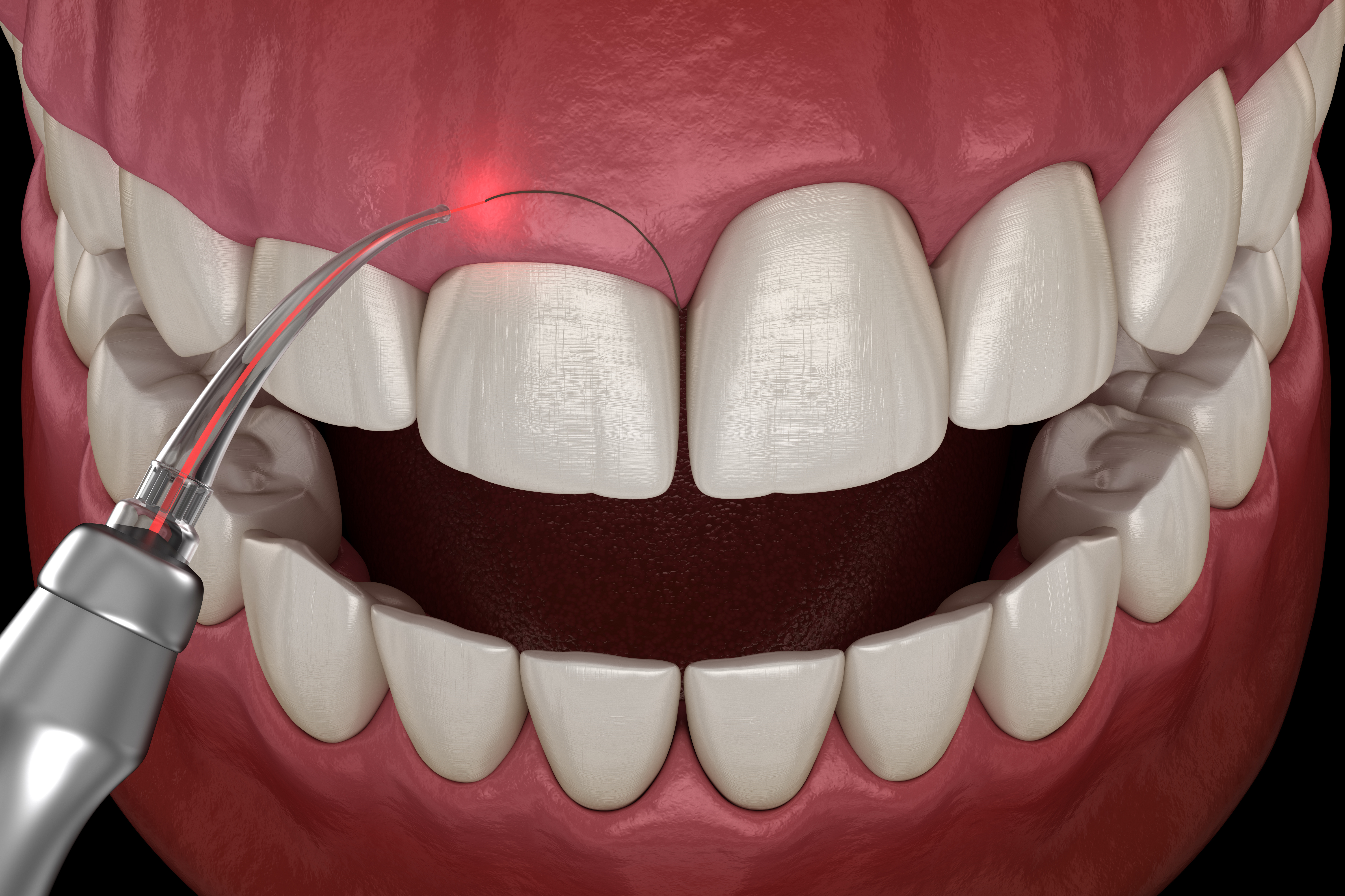
LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure) is a modern, minimally invasive treatment for periodontitis. It uses a specialised laser to target and remove diseased gum tissue while preserving healthy tissue. This technique eliminates harmful bacteria, reduces gum inflammation, which may support tissue healing and attachment in selected clinical cases. LANAP may be associated with reduced discomfort and recovery time in selected patients.
LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
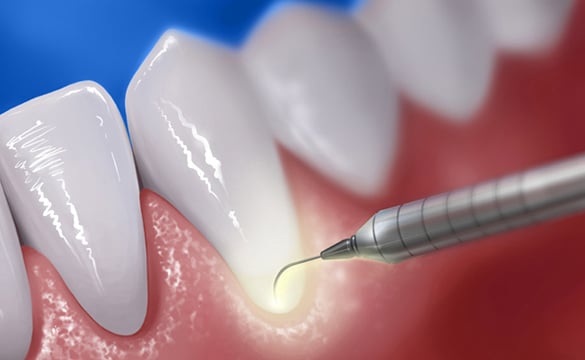
Root Planing
Professional dental cleaning is vital for removing dental plaque and tartar, especially effective for mild gum disease. Using specialised tools, this process cleans roots below the gum line and helps remove plaque, which is crucial in the early stages to prevent further inflammation and protect teeth. Root planing is also preventative for those with healthy gums.
Root Planing
.%20Medically%20accurate%203D%20illustration%20of%20human%20teeth%20treatment.jpeg)
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are employed in the management of gum diseases to target bacterial infections that contribute to periodontal issues. They can be administered systemically or placed locally in the gum pockets to reduce infection and inflammation, aiding in the healing process and used adjunctively with other periodontal treatments to optimise outcomes.
Antibiotics

Surgical Treatments
Gum Contouring
Gum contouring helps to reshape excessive or uneven gums. Utilising surgical techniques, it trims away excess gum tissue to reveal more of the teeth, or adds tissue where needed. This surgery not only improves gum health by removing overgrowth but also addresses gum shape and contour based on functional and aesthetic considerations.
Gum Contouring
Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation
Pinhole gum rejuvenation is a minimally invasive technique to treat gum recession. Unlike traditional grafting, it involves creating a small hole to reposition the gum tissue. The procedure requires no stitches or significant incisions, which may be associated with a shorter recovery period in selected cases. It covers exposed roots, reduces sensitivity, and enhances the appearance of the gums, contributing to overall dental health and a more pleasing smile.
Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation
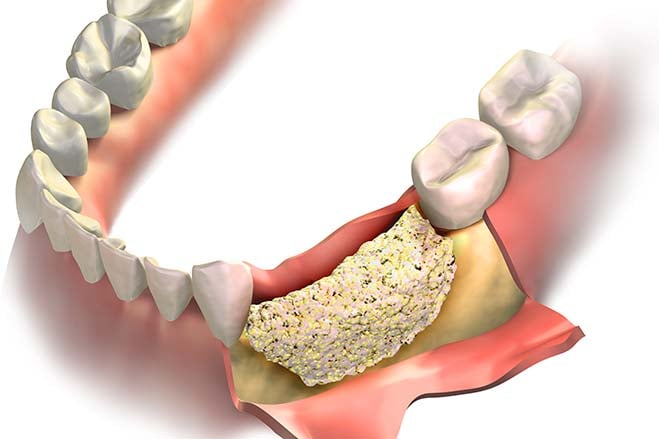
Dental Bone Graft
Dental bone grafting aims to restore or correct bone tissue in the area of the teeth. It may in the transplantation of your own bone material or synthetic materials, such as gum grafting. This enables the restoration of the jaw bone, the support of teeth, and the creation of a suitable foundation for tooth implantation.
Dental Bone Graft
Soft Tissue Graft
Soft tissue grafts involve transplanting healthy, pinkish soft tissue to areas suffering from recession, enhancing gum coverage on teeth. This procedure not only improves the aesthetic appearance but also mitigates sensitivity and protects the teeth roots from decay, contributing significantly to gum health and stability.
Soft Tissue Graft

Periodontal Surgery (e.g., Open Flap Debridement or OFD)
These are surgical procedures aimed at restoring and maintaining healthy gums. They include the removal of diseased tissues, treatment of pockets between teeth and gums, as well as correction of receding gums. One example is Open Flap Debridement (OFD), a type of pocket reduction surgery involving the surgical opening of gum tissue to remove plaque and tartar from deep periodontal pockets. Surgery is directed toward gum disease treatment, to manage periodontal disease and support gum health.
Periodontal Surgery (e.g., Open Flap Debridement or OFD)
Bone Surgery
Bone surgery in periodontal treatment reshapes the jawbone marred by disease, often following deep cleaning procedures. This surgery addresses craters and defects in the bone, facilitating the reattachment of gums to the bone, which can be crucial in advanced stages of gum disease.
Bone Surgery

Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR)
This technique encourages the natural regrowth of bone and gum tissue lost to periodontal disease. By placing a biocompatible barrier (material that's compatible with living tissue; prevents adverse reactions) between the bone and gums, it allows bone cells to proliferate, leading to increased support for teeth, which may help support bone regeneration in selected cases.
Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR)
Tissue-Stimulating Proteins
Tissue-stimulating proteins are biomolecules used in dentistry to promote tissue regeneration and healing, particularly in periodontal therapy. They stimulate the body's natural mechanisms for tissue repair by encouraging the growth of new blood vessels, bone, and connective tissue. These proteins can be applied locally to affected areas or incorporated into grafting materials to enhance the success of procedures such as bone and soft tissue grafts, ultimately improving overall oral health outcomes.
Tissue-Stimulating Proteins
Treatment Methods Of Gum Disease in 2026:
| Gum Disease Type | Treatment Methods |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Professional Cleaning: Early stages of gingivitis can often be reversed with professional dental cleaning. |
| Periodontitis | Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning): This non-surgical procedure involves cleaning below the gum line to remove plaque and tartar and smoothing the tooth root to help the gums reattach. |
| Advanced Periodontitis | Extensive Periodontal Therapy: Involves a more aggressive treatment strategy including scaling and root planing, local delivery of antimicrobials, systemic antibiotics, and multiple surgical procedures such as flap surgery/pocket reduction surgery, guided tissue regeneration, and possibly bone grafting to attempt to salvage the remaining periodontal structure and teeth. |
| Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG) | Antibiotics and Professional Cleaning: Treatment often includes antibiotics to control infection, professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar, and specialised mouth rinses to soothe the gum tissue. |
Concerned about your oral health? Explore your options with professionals from Nuffield Dental.
How is Gum Disease Diagnosed?
Your dentist can diagnose periodontitis and its severity through various methods:
Step 1 : Medical History Review
Analysing your medical background, including lifestyle habits like smoking or medication use that can cause symptoms like dry mouth, is crucial.
Step 3 : Gum Pocket Measurement
Using a small measuring instrument known as a dental probe, your dentist will measure the space between your gums and around your teeth themselves. This is done at multiple points in both your upper and lower gums. Normally, the depth of these pockets ranges from 1 to 3 mm. A depth exceeding 4 mm can suggest periodontitis, and those beyond 5 mm may not be effectively treated with regular dental care.
Step 2 : Oral Examination
A thorough check for plaque and tartar accumulation is performed, along with assessing any tendency for your gums to bleed easily.
Step 4 : Dental X-Rays
These are taken to examine any bone loss, especially in areas with deeper gum pockets.
Based on the findings, your dentist will classify the stage and grade of periodontitis, considering the disease's severity, treatment complexity, risk factors, and your overall health.
Gum Disease Treatment Procedure
Before the Procedure
Preparing for gum disease treatment involves a few key steps to ensure a smooth and effective process:
- Gum Specialist Examination: The specialist measures pockets in the gums for an accurate diagnosis, assessing oral health and the extent of gum disease to craft a treatment plan.
- Medical History Discussion: Identifying symptoms of gum disease informs potential complications and aids in treatment planning.
- Gum Treatment Plan Development: A dental hygienist tailors a treatment strategy based on the diagnosis, outlining necessary steps and timelines.
- Procedure Explanation: Detailed information about the treatment is provided, clarifying what to expect and the associated risks.
- Local Anaesthesia Discussion: Anaesthesia options are tailored to the procedure and personal health, with extra care for those with heart disease or chronic infection.
- Patient Preparation: Instructions are given, possibly including temporary fasting before the treatment.
During the Procedure
The gum treatment process includes:
- Local Anaesthesia Application: To numb the area and ensure patient comfort without pain.
- Deep Hygiene Cleaning: Ultrasonic scalers and hand instruments (for more detailed cleaning) are used to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line, and smooth out rough areas on the root surfaces. A pinhole will be created in the receding gum tissues. Collagen strips will be inserted into the pinhole to keep the gums steady and help create novel tissue, ultimately securing the gums in place.
- Periodontal Surgical Procedures: Necessary for some patients, like gum surgery, tissue grafting, or bone grafting to repair tissues. Gum Contouring, a minor surgery, is performed to use
gum from a different part of the mouth to restore the infected area undergoing gum recession. Soft tissue healing typically occurs over several weeks, depending on individual response, which may help reduce sensitivity and support gum stability. - Maintaining Comfort: The medical team ensures the patient is at ease, providing ongoing explanations throughout the treatment.
After the Procedure
- Post-Treatment Care Instructions: The doctor outlines what occurred, advises on care, and addresses discomfort
- Gum Care Guidelines: Include using a soft toothbrush, gentle cleaning, and mouth rinsing with special solutions.
- Dietary and Lifestyle Cautions: Avoiding items that hinder healing; following prescriptions as directed.
- Follow-Up Visits: Scheduled to monitor healing, remove stitches, and adjust treatment.
- Doctor-Patient Collaboration: Essential for recovery and preventing gum disease recurrence, with emphasis on adherence to care instructions and regular check-ups.
Follow-up Appointments
Key aspects of follow-up visits include:
- Healing Progress Assessment: The doctor checks soft tissue healing, looking for pinkish tissue and signs of swelling or bleeding to gauge treatment success and decide if additional procedures are needed for loose gums.
- Stitch Removal: The doctor may remove stitches that don't dissolve on their own and assess the connective and gum tissues' condition.
- Treatment Adjustments: Based on ongoing assessments, the doctor might perform corrections or additional procedures if tissue regeneration or bone grafting hasn't been successful.
- Care and Hygiene Education: The doctor advises on home care and hygiene for root surfaces, possibly including the use of an irrigator.
- Health Maintenance Planning: A long-term care plan is tailored, encompassing regular check-ups, diet advice, and any necessary procedures.
- Monitoring for Recurrences: The doctor checks bone health and looks for signs of potential gum disease recurrence to prevent it.

Benefits of Gum Disease Treatment
Here are some important benefits of treatment:
Who is a Good Candidate For Gum Disease Treatment?
Periodontal treatment benefits both adults and children, and may support timely management through regular dental care. If you’re experiencing any related signs or symptoms, a dental assessment is recommended.
- Inflammation and bleeding. Patients with signs of gum inflammation, bleeding, and swelling should receive timely assistance to prevent the progression of the periodontal disease.
- Sensitivity and pain. Individuals experiencing sensitivity, pain, or discomfort in the gum area may need treatment to alleviate symptoms.
- Aesthetic changes. Patients noticing aesthetic imperfections such as changes in gum shape may benefit from treatment to alleviate discomfort.
Unsure as to how periodontal treatment can benefit you? Book an appointment with Nuffield Dental: we'll get in touch.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum diseases is easier than treating them, as advanced stages can threaten chewing function. Here are some recommendations that may help:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and use dental floss to remove dental plaque. Avoid applying excessive pressure while brushing.
- Incorporate dental floss or interdental brushes into your daily routine to clean the spaces between your teeth.
- Use antiseptic mouthwashes to rinse your mouth and reduce bacterial activity around your teeth.
- Schedule preventive check-ups and cleanings with your dentist at least once every six months.
- Maintain a balanced diet with nutritious foods including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products to support gum health.
- Reduce consumption of sugars and acidic foods contributing to dental plaque formation.
- Quit smoking, as it is a risk factor for gum diseases.
- Monitor your overall health and promptly seek dental attention at the first signs of problems.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Gum Disease Treatment Risks
Risks of gum disease treatment include:
- Temporary pain, sensitivity, or discomfort, particularly after surgical procedures.
- Short-term gum inflammation and swelling following treatment.
- Temporary sensitivity of teeth to temperature and pressure.
- Minor and usually temporary bleeding.
- Allergic reactions to materials or medications used.
Gum Disease Treatment Risks

Gum Disease Treatment Complications
- Infections can sometimes occur as a complication of treatment.
- For dental implants, peri-implantitis is a potential complication that’s characterised by gum inflammation and bone loss around the implant.
At Nuffield Dental, treatments are provided by registered dental professionals following established clinical protocols.
Gum Disease Treatment Complications

Gum Disease Treatment Cost in 2026
The cost of treating gum diseases in Singapore can vary significantly depending on the type of procedures performed, the complexity of the periodontal disease, and the chosen clinic.
| Gum Disease Treatment | Estimated Costs (SGD) |
|---|---|
| Scaling and Polishing | $100 - $300 |
| Root Planing | $200 - $600 |
| Antibiotics | $20 - $100 |
| LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure) | $1,000 - $3,000 |
| Soft Tissue Graft | $1,500 - $3,000 |
| Gum Contouring | $800 - $2,500 |
| Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation | $1,500 - $3,500 |
| Periodontal Surgery (e.g., Open Flap Debridement) | $2,000 - $4,000 |
| Bone Surgery | $2,000 - $4,500 |
| Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) | $1,500 - $4,000 |
| Dental Bone Graft | $1,000 - $4,000 |
| Tissue-Stimulating Proteins | $500 - $2,000 |
Note that these estimates may not include the cost of consultations, medications and other miscellaneous items.
Earlier intervention may improve treatment outcomes and reduce disease progression. A dental consultation can help determine appropriate treatment options. All fees are subject to prevailing Singapore Goods and Services Tax. Fee adjustments may apply depending on the number of teeth treated.
Are There Subsidies for Gum Disease Treatment?
Yes. In Singapore, you may be able to claim for gum disease treatment under Medisave or CHAS (Community Health Assist Scheme). Medisave covers certain surgical treatments such as guided bone regeneration, but not non-surgical ones like scaling and polishing. For CHAS, depending on the colour of your card (orange, blue, red or crimson), you may be able to receive subsidies for treatments like scaling and polishing.
At Nuffield, we’re partnered with a number of insurance providers, so you may be able to offset your bill using your plan.

Why Should I Choose Nuffield for Gum Disease Treatment in 2026?
- Nuffield Dental provides access to Chao Pinhole Gum RejuvenationⓇ for selected clinical cases.
- A patient-specific approach tailored to the specific stage of gum disease (e.g., Gingivitis or Periodontitis). We are committed towards properly diagnosing patients and matching them with the appropriate treatments.
- The use of gum treatment technologies that align with current medical protocols.
- Adherence to recognized standards for quality and hygiene in providing dental services. At Nuffield Dental, we mandate that our dental nurses undergo formal staff training quarterly. Moreover, frequent training sessions are conducted in our dedicated in-house training centre by designated and accredited senior nurses.
Our Team of Dentists at Nuffield Dental
Gum treatment at Nuffield Clinic is conducted by our dental specialists who manage a range of periodontal conditions. Here are two names to look out for:
Gum Disease Treatment: Before and After Photos
Speak with the clinic team for general information about treatment approaches and outcomes.
Note: Before-and-after photos are not displayed publicly in accordance with MOH advertising guidelines. Patients may view clinical results during consultations.
FAQs
What are the Early Signs of Gum Disease?
Early signs of gum disease include gum redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing. Additionally, bad breath and a persistent bad taste in the mouth are common indicators. Recognizing these early symptoms is key to seeking timely treatment.
Is Gum Disease Contagious?
The bacteria causing gum disease can be spread through saliva. However, the development of the disease depends on individual health factors, including oral hygiene and overall health. It's important to maintain good oral hygiene to reduce the risk of transmission.
Can Gum Disease be Reversed?
Yes, early intervention with dental care can often halt or reverse the early stages of gum disease.
When is it Too Late to Reverse Gum Disease?
It's never too late to seek medical assistance. W hen advanced periodontitis develops, conservatively saving all teeth and restoring gum health becomes impossible. Once periodontitis sets in, reversing gum disease is difficult, but treatment can prevent further damage.
How Can I Treat My Gum Disease Myself?
Treating gum disease on your own is not possible. It's essential to seek help from a qualified dentist, as only professionals have the equipment that can facilitate deep cleaning.
How Long Will the Procedure Take?
The duration of gum disease treatment sessions varies by procedure:
- Professional cleaning: Typically 30-60 minutes.
- Scaling and root planing: 45-90 minutes per quadrant, often over multiple visits.
- Surgical procedures (e.g., flap surgery, grafts): 1-2 hours, depending on complexity.
- Laser treatment: Varies, usually around an hour.
Can I Resume Daily Activities After Gum Disease Treatment?
Yes. Post-treatment, most daily activities can be resumed immediately, though surgical procedures may require a brief period of rest and limited activity.
Can Diet Affect Gum Disease?
Yes, a nutrient deficiency like calcium and iron negatively impacts gum health. Additionally, excessive consumption of sweets and acidic foods can trigger the disease. A balanced diet supports gum health, while sugary and acidic foods can worsen gum disease.
What is the Difference Between a Dentist and a Periodontist?
A dentist offers general oral care, while a periodontist is a dentist that specialises in treating gum disease.
Can I Live With Untreated Gum Disease?
Yes, but it’s not ideal as the disease will gradually progress, causing pain and discomfort. In advanced stages, you may lose teeth and chewing function. Untreated gum disease leads to complications, but managed care can maintain oral health.
Will I Lose My Teeth if I Have Periodontal Disease?
Without treatment, it's possible to lose all teeth due to periodontitis. However, seeking timely help from specialists can help preserve your natural teeth. Early and effective treatment can often prevent tooth loss from periodontal disease.
The Nuffield Dental Clinic Network In Singapore
Seletar Dental
Nuffield Dental Seletar
Greenwich V
1 Seletar Road #01-07/08
Singapore 807011

Kovan Dental
Nuffield Dental Kovan
Simon Plaza
2 Kovan Road #01-03
Singapore 548008

Serangoon Dental
Nuffield Dental Serangoon Gardens
Serangoon Garden Estate
57 Serangoon Garden Way
Singapore 555953

Siglap Dental
Nuffield Dental Siglap
The Domain
914 East Coast Road #01-03
Singapore 459108

Bedok Dental
Nuffield Dental Simpang Bedok
East Village
430 Upper Changi Road #01-64
Singapore 487048

Holland Village Dental
Nuffield Dental Holland Village
7 Holland Village Way #03-16
Singapore 275748

Jurong East Dental
Nuffield Dental Westgate
Westgate
3 Gateway Dr #04-32
Singapore 608532

HarbourFront Dental
Nuffield Dental HarbourFront
HarbourFront Centre
1 Maritime Square #02-64A
Singapore 099253

Orchard Dental
Nuffield Dental Jewel
Wheelock Place
501 Orchard Road #05-01
Singapore 238880

Raffles Place Dental
Nuffield Dental Raffles Place
One Raffles Place
1 Raffles Place #05-19
Singapore 048616


Book an Appointment
Fill out the form for any request or questions you have and we will contact you within one working day..


Why Choose Nuffield Dental?
Nuffield Dental is a one-stop, multi-disciplinary dental care centre in Singapore. At Nuffield, we put you first. We believe in providing personalised service for each patient.
Nuffield Dental is a one-stop, multi-disciplinary dental care centre. Here at Nuffield Dental, we pride ourselves of our personalised oral care for each and every one of our patients. We need to make sure you get all the help you need to make your dental procedures comfortable, accessible and seamless.
Our dentists have been accredited in gum treatment and oral surgery for 20+ years. We have accredited dental providers who are skilled in the area of dental implant surgery.
Articles
The newest and best lifestyle articles selected by our editorial team.

- 17 Nov 2025
- 2 mins read
Current scientific evidence does not show a conclusive connection between intact dental amalgam fillings and symptoms such as brain fog, chronic...

- 17 Nov 2025
- 2 mins read
The Minamata Convention on Mercury established 2034 as the global target year to end the use of dental amalgam. While this may seem gradual, the...

- 17 Nov 2025
- 2 mins read
Dental amalgam has been used in restorative dentistry for more than 150 years. It has long been regarded as a durable and practical material....
.png?width=2223&height=447&name=Background%20(4).png)





.jpg)

.png)

.png)



